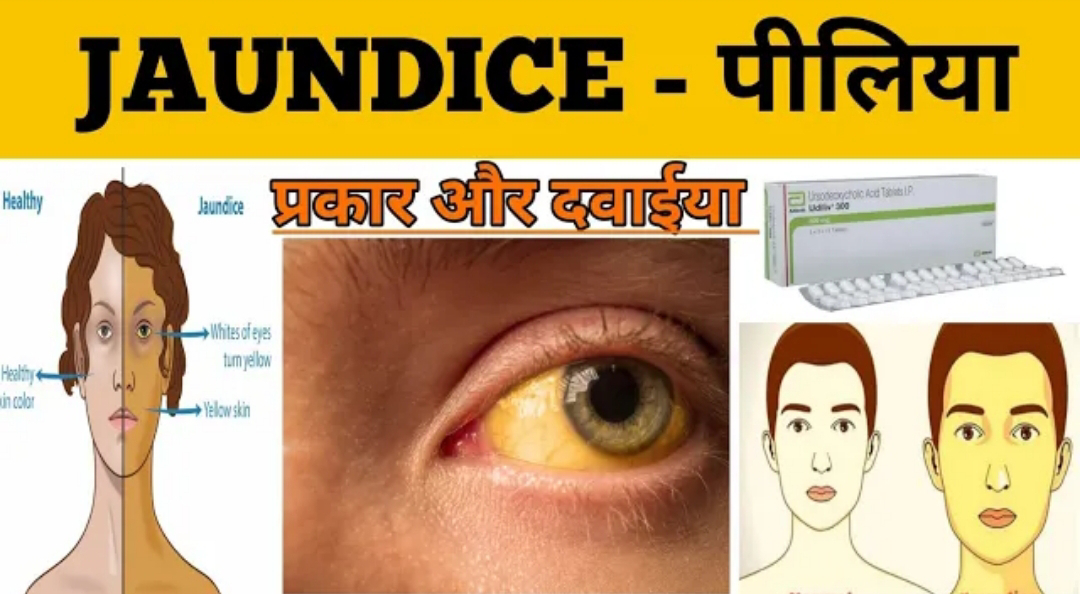
### Types of Jaundice:
1. **Hepatocellular Jaundice:** This type of jaundice occurs when there is a liver disease that impairs the liver's ability to process bilirubin.
2. **Hemolytic Jaundice:** Hemolytic jaundice results from the excessive breakdown of red blood cells, leading to increased bilirubin production.
3. **Obstructive Jaundice:** This type of jaundice is caused by an obstruction in the bile ducts, which prevents the proper excretion of bilirubin.
### Symptoms of Jaundice:
1. Yellowing of the skin and eyes
2. Dark urine
3. Pale stools
4. Itchy skin
5. Abdominal pain
6. Fatigue
7. Nausea
### Main Causes of Jaundice:
1. **Liver Diseases:** Hepatitis, cirrhosis, and other liver conditions can lead to jaundice by affecting the liver's ability to metabolize bilirubin.
2. **Hemolytic Disorders:** Conditions that cause increased breakdown of red blood cells, such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia, can raise bilirubin levels.
3. **Bile Duct Obstruction:** Tumors, gallstones, or other conditions that block the bile ducts can prevent the proper excretion of bilirubin, leading to jaundice.
### Treatment of Jaundice:
The treatment of jaundice depends on the underlying cause. Treatment may involve addressing the specific condition causing jaundice, such as medications for liver diseases, surgery for bile duct obstructions, or managing hemolytic disorders. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications and alcohol abstinence may also be recommended.
It's important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment if you suspect you have jaundice.
### Additional Information:
### Diagnosis of Jaundice:
1. **Blood Tests:** Blood tests can help determine the levels of bilirubin in the blood and identify any underlying liver or blood disorders.
2. **Imaging Studies:** Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can help identify any blockages or abnormalities in the liver or bile ducts.
### Complications of Jaundice:
1. **Acute Liver Failure:** In severe cases of liver disease causing jaundice, there is a risk of acute liver failure, which can be life-threatening.
2. **Gallstones:** In obstructive jaundice, the blockage in the bile ducts can lead to the formation of gallstones.
### Prevention of Jaundice:
1. **Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle:** Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol consumption can help maintain a healthy liver.
2. **Vaccination:** Vaccination against hepatitis A and B can help prevent liver infections that can lead to jaundice.
### Home Remedies for Jaundice:
1. **Stay Hydrated:** Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins from the body.
2. **Herbal Remedies:** Some herbs like dandelion root, turmeric, and ginger are believed to have benefits for liver health.
### When to See a Doctor:
If you experience symptoms of jaundice such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, or abdominal pain, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Prompt medical attention is crucial for identifying the underlying cause and initiating appropriate treatment.
Remember, jaundice is a symptom of an underlying condition and not a disease in itself. Proper diagnosis and treatment of the root cause are essential for managing jaundice effectively.




0 Comments